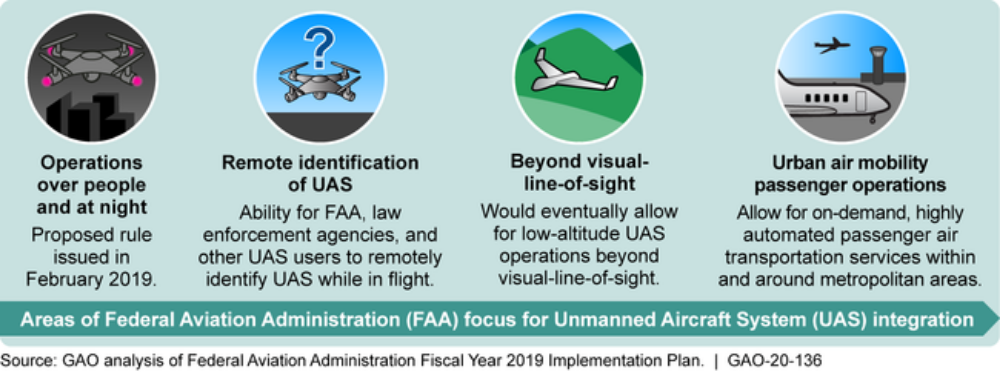
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has undertaken actions to integrate unmanned aircraft systems (UAS or “drones”) into the national airspace and has developed plans to allow for increasingly complex operations, including operations over people and beyond visual-line-of-sight and—eventually—passenger operations (see figure).
However, FAA efforts to track related costs may result in incomplete information. FAA established a means of tracking the costs associated with some UAS-activities in certain offices, but many, if not all, FAA offices are doing work related to both manned aviation and UAS. FAA officials stated that they do not know or plan to assess the extent to which staff who split their time between UAS-activities and other responsibilities are tracking those costs.
Furthermore, FAA’s future costs to conduct oversight and provide air navigation services are largely unknown due to the changing nature of the industry and its early stage of development. Ensuring that information on UAS-related costs is complete and reliable now could put FAA in a better position to identify those costs as they evolve and possibly expand in the future.
The extent to which FAA should recover costs for its UAS-related activities, and what fees are appropriate, are policy decisions for the administration and Congress. Accordingly, this report does not recommend any specific fee mechanism. Nonetheless, planning and consideration of policy goals, using available guidance on user fee design, could better position FAA to inform future decision-making on these issues as it proceeds with UAS integration.
Since 2015, FAA has collected a registration fee from UAS operators, but most of FAA’s UAS costs are not related to registration or covered by this fee. A stakeholder group established by FAA identified potential fee mechanisms and concluded in 2018 that the aviation industry, FAA, and Congress should identify revenue streams to help fund FAA’s UAS activities. Further, GAO guidance and Office of Management and Budget instructions provide a framework, including information requirements, for designing effective user fees.
FAA officials said that they have not considered user fee mechanisms as part of their planning because they have been awaiting this report to inform their decision-making. By using available guidance as part of its planning, FAA could incorporate steps, such as identifying costs and beneficiaries, which would benefit future fee design considerations.
UAS have the potential to provide significant social and economic benefits in the United States. FAA is tasked with safely integrating UAS into the national airspace. As the UAS sector grows, so do demands on FAA’s staffing and other resources to develop, oversee, and enforce rules and systems needed to safely integrate UAS into the national airspace.
The FAA Reauthorization Act of 2018 provides for GAO to review issues related to establishing fee mechanisms for FAA to recover its costs related to UAS. This report discusses, among other things, 1) FAA efforts to track the costs of current and planned activities related to UAS and 2) key considerations and options for designing user fee mechanisms that could recover FAA’s costs. GAO reviewed FAA documents and financial data for fiscal years 2017 through 2019 and industry reports on drone integration funding. GAO interviewed a non-generalizable sample of 22 UAS industry stakeholders, selected based on participation in FAA advisory groups or prior GAO knowledge to achieve a range of perspectives. GAO reviewed its guidance on designing effective fee mechanisms and OMB instructions to agencies about implementing user fees.
What GAO Recommends
GAO is recommending that FAA (1) implement a process to ensure UAS-related cost information is complete and (2) use available guidance on effective fee design to incorporate steps, as part of UAS integration planning, that will inform future fee design considerations. FAA concurred with the recommendations.
The full report is available here.
Source: Press Release