has been granted a patent for a system that improves the performance of vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aerial vehicles. The system includes two GPS antennas and a flight controller that utilizes the GPS signal from the antenna that is not being used for navigation when the vehicle is at a certain pitch level. The system also detects errors in the GPS antennas and adjusts the pitch level to minimize the use of the antenna with the error.
AeroVironment: Recent Patent Grants
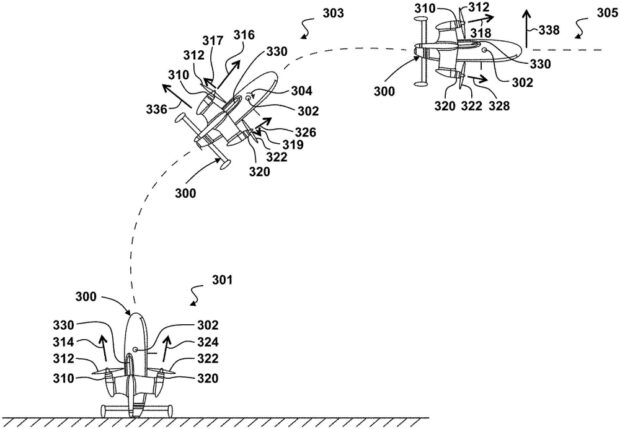
A recently granted patent (Publication Number: US11686859B2) describes a system for a vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aerial vehicle that utilizes GPS signals from multiple antennas to improve flight control. The system includes an aerial vehicle flight controller with a processor and addressable memory. The flight controller receives the pitch level of the VTOL aerial vehicle from sensors during vertical flight and determines if the pitch level is at a set rotation from vertical. If the pitch level is at or above the set rotation, the system utilizes a GPS signal from either a first GPS antenna or a second GPS antenna, using a GPS antenna switch.
The system also detects errors in the GPS antennas and adjusts the set rotation to minimize the use of the antenna with the error. This prevents inadvertent switching between the antennas during various VTOL aerial vehicle maneuvers such as ascent, descent, evasive action, and banked turns. The first GPS antenna is located in the nose of the VTOL aerial vehicle, while the second GPS antenna is positioned distal from the first antenna. The area between the first GPS antenna and the exterior surface of the nose is clear of any carbon-based or metallic material.
The first GPS antenna has a center field of view that is oriented vertically when the VTOL aerial vehicle is in a nominal steady state hover attitude or a nominal steady state attitude for vertical flight. The second GPS antenna has a center field of view that is oriented vertically when the VTOL aerial vehicle is in a nominal pitch attitude for horizontal flight. The flight controller is in communication with the GPS antenna switch and the aerial vehicle sensors, allowing it to utilize the GPS antenna signal via the switch.
Additionally, the system includes a primary GPS receiver and a secondary GPS receiver in communication with the flight controller. The flight controller can switch between the receivers based on factors such as signal quality and the number of satellites in the visible constellation of each receiver.
Overall, this patented system enhances the flight control of VTOL aerial vehicles by utilizing multiple GPS antennas, detecting errors, and adjusting the set rotation to optimize GPS signal usage.
Source: Army Technology