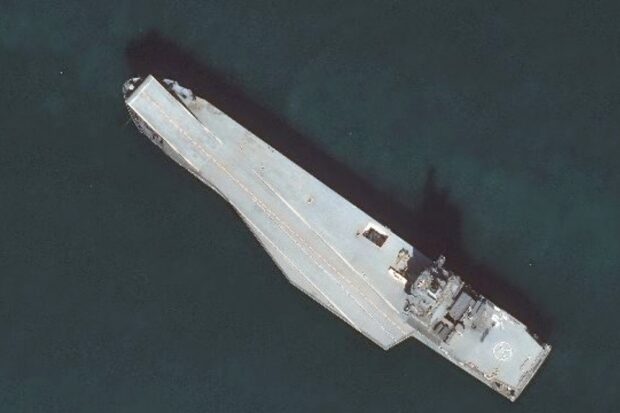
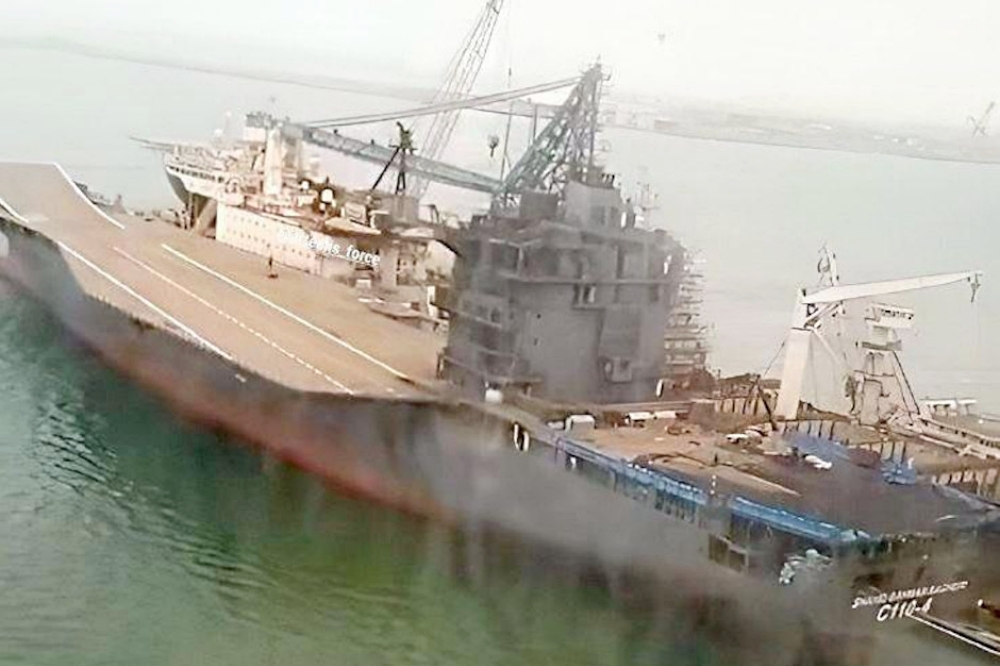
Analysis from November and December 2024 suggests that Iran’s Shahid Bagheri drone carrier has likely commenced its first sea trials, signaling a critical juncture in the country’s ongoing efforts to modernize its navy and expand its capabilities in asymmetric naval warfare.
This development marks a key moment not only for Iran but also for the broader geopolitical landscape in the Persian Gulf and beyond.
The Shahid Bagheri is designed to carry and deploy a range of unmanned aerial vehicles [UAVs], including surveillance and reconnaissance drones, as well as more sophisticated strike drones. Among the most prominent UAVs are those from the Shahed family, which have already proven their effectiveness in both reconnaissance and precision strike missions in regional conflicts.
Equipped with advanced command and control systems, the Shahid Bagheri can coordinate the operations of multiple UAVs simultaneously, allowing for greater operational flexibility and strategic depth. This makes the ship a key asset in Iran’s efforts to enhance its naval power in an increasingly contested region.
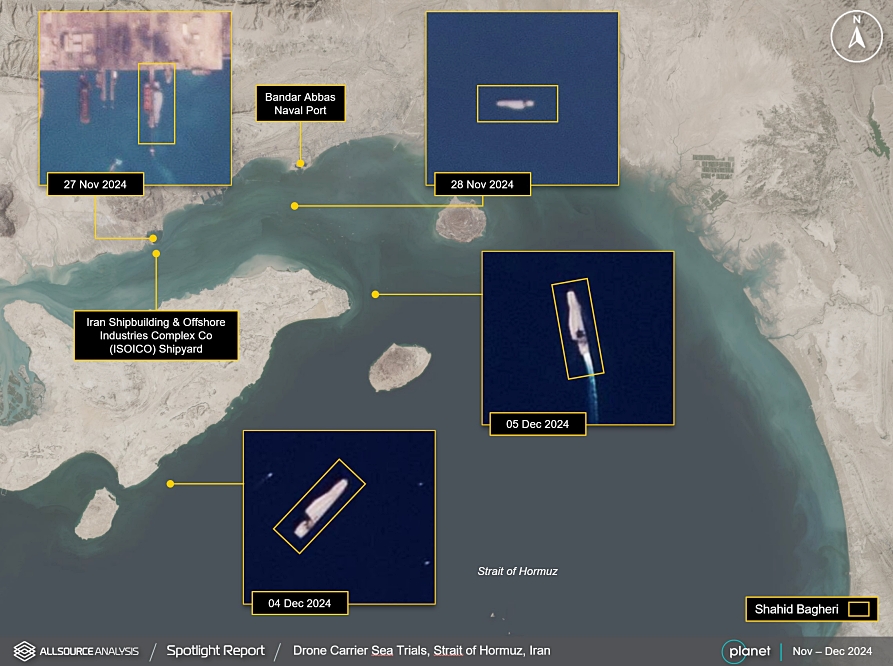
GEOINT analysis from November – December 2024 shows the Iranian Drone Carrier Shahid Bagheri likely undergoing its first sea trials – X
In addition to reconnaissance and surveillance, the UAVs deployed by the Shahid Bagheri could also perform offensive operations, potentially launching precision strikes against high-value maritime or land-based targets.
Such capabilities would allow Iran to project power far beyond its shores, enabling it to conduct operations with minimal risk to personnel and maximizing its ability to inflict damage on adversary forces. This would significantly enhance Iran’s ability to defend its territorial waters and extend its influence in maritime conflict zones.
The Shahid Bagheri fits into a broader strategy by Iran to modernize and diversify its naval forces. Over the past decade, the country has increasingly focused on asymmetric naval tactics, including the development of smaller, fast-moving vessels and unconventional platforms.
By integrating UAVs into its naval strategy, Iran is adding a crucial element to its already diverse fleet of assets. The ship’s relatively small size, combined with the versatility of drones, makes it a highly flexible asset, capable of operating in contested waters with less reliance on traditional large surface combatants or support infrastructure.
The impact of the Shahid Bagheri on regional naval dynamics could be profound. The introduction of a drone carrier provides Iran with the ability to deploy UAVs for both reconnaissance and offensive operations in vital maritime chokepoints such as the Strait of Hormuz, the Bab el-Mandeb Strait, and the Gulf of Oman.
The potential for Iran to use these UAVs to gather intelligence, conduct surveillance, or even launch strikes without exposing personnel to direct danger would make it a formidable presence in the region, forcing regional powers to adapt their strategies.
While the Shahid Bagheri is still undergoing sea trials, its existence and potential deployment represent a significant shift in how Iran plans to project its naval power. The ship’s ability to operate independently, with its fleet of drones, offers Iran the flexibility to extend its reach beyond its immediate maritime boundaries.
This could lead to a rethinking of regional security strategies, as countries in the Gulf and the broader Middle East reassess how best to respond to this new capability.Despite its potential, the deployment of the Shahid Bagheri raises several operational and technological challenges for Iran. While the country has demonstrated impressive technical advancements in UAV development, the integration of drone operations into a naval context is an entirely new challenge.
The coordination of multiple UAVs from a single platform requires not only sophisticated communication systems but also reliable logistical support. The need for real-time data analysis and the capacity to make rapid decisions on drone deployment will demand a high level of coordination between Iran’s naval and air forces.
The challenges are not limited to technical issues. The Shahid Bagheri will also have to contend with the broader operational requirements of maintaining a fleet of drones and ensuring their effectiveness in various maritime environments.
While Iran has been investing in developing a more flexible and elusive naval force, the true test of the Shahid Bagheri will be how well it can integrate its UAV operations with existing naval assets, particularly in high-intensity conflict scenarios.
How well Iran can establish robust communications networks and logistic chains for drone deployment in contested waters will be a key determinant in the success of the drone carrier.
Furthermore, international reactions to the Shahid Bagheri and its potential deployment could escalate geopolitical tensions. The introduction of such a capability will undoubtedly attract attention from neighboring Gulf states, Western powers, and international organizations monitoring Iran’s military advancements.
The growing capabilities of Iran’s naval forces, particularly with the advent of a drone carrier, could lead to new diplomatic initiatives aimed at limiting Iran’s military reach or imposing sanctions designed to curb its defense technology developments.
The Shahid Bagheri is not only a technological advancement but also a part of a broader strategic shift by Iran. The country has long sought to modernize its military and make use of cutting-edge technologies to counteract the technological superiority of Western powers and regional adversaries.
In addition to the Shahid Bagheri, Iran has also been working on the development of new submarines, including the Fateh and Ghadir, which further complement its asymmetric warfare strategy. These developments demonstrate Iran’s desire to create a diversified, flexible naval force capable of responding to a range of threats in the region.
Looking ahead, the Shahid Bagheri could play a key role in scenarios far beyond the Persian Gulf. The growing prevalence of drone warfare globally, especially among rising naval powers, suggests that the concept of drone carriers may become more common.
The Shahid Bagheri could serve as a model for other countries seeking to extend their naval reach with cost-effective, scalable platforms that do not require the extensive support infrastructure of traditional aircraft carriers.
In the future, Iran may leverage this technology to project power into other regions, such as the Red Sea, the Indian Ocean, or even the Mediterranean, where its mobility would be an advantage in contested waters.
Moreover, the relatively small size of the Shahid Bagheri compared to traditional aircraft carriers offers another advantage: mobility. This makes it easier for Iran to deploy the ship in areas where larger warships would be at a disadvantage.
The ship’s limited need for support infrastructure and its ability to quickly relocate allow it to exert influence in distant regions with less logistical burden. This capability could give Iran a more agile and responsive naval presence, capable of rapidly adapting to changing geopolitical dynamics and conflicts.
The development of the Shahid Bagheri is a significant milestone for Iran’s naval strategy. As drone warfare continues to evolve, this platform could offer Iran a more cost-effective and scalable way to extend its naval reach. As the system matures and Iran continues to develop its capabilities in drone warfare, we can expect further advancements in both military technology and Iran’s geopolitical influence.
Source: Bulgarian Military;


