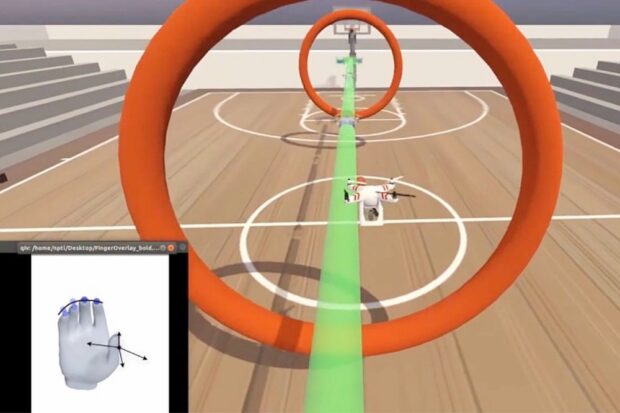
Researchers at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor have developed a device that let a 69-year-old man with paralysis fly a virtual drone using only his thoughts.
The brain–computer interface (BCI) decoded the man’s brain activity as he imagined moving three groups of digits in real time. By associating neural signals with the movements of multiple fingers, the work builds on previous BCI research, most of which has focused on moving a single computer cursor or whole virtual hand. The feat offers hope that BCIs could one day help people with paralysis to perform a wider range of activities, such as typing or playing complex video games.
“There’s a lot of things that we enjoy or do as humans where we use multiple individuated finger movements, so like typing, sewing, playing a musical instrument,”
says study co-author Matthew Willsey, a neurosurgeon at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor.
“That’s what this line of work is focused on, how we enable the control of multiple things at the same time.”
The study, published on 20 January in Nature Medicine, was inspired by the participant’s own request to use a BCI to fly a drone. He told the researchers that controlling the virtual object was like playing a musical instrument.
“Flying it is tiny little finesses off a middle line, a little bit up, a little bit down,” he said.
The research was published in a paper entitled ‘A real-time, high-performance brain-computer interface for finger decoding and quadcopter control’ that can be accessed here.
Source: Nature