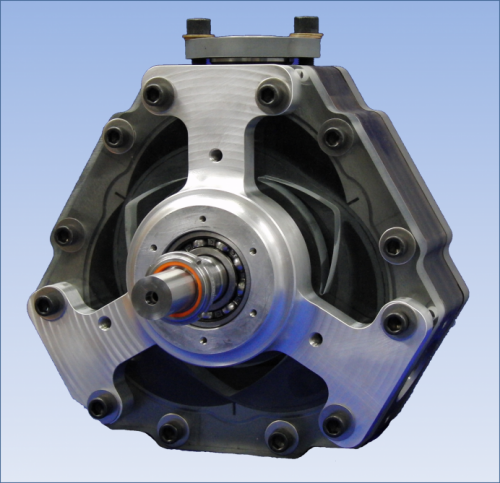
 The internal combustion engine (ICE) has had a remarkably successful century and a half. Unfortunately, it’s notoriously inefficient, wasting anywhere from 30 to 99 percent of the energy it produces and spewing unburned fuel into the air.
The internal combustion engine (ICE) has had a remarkably successful century and a half. Unfortunately, it’s notoriously inefficient, wasting anywhere from 30 to 99 percent of the energy it produces and spewing unburned fuel into the air.
Last week, Gizmag interviewed Dr. Alexander Shkolnik, President and CEO of LiquidPiston, Inc. about the company’s LiquidPiston X2 – a 40-bhp rotary engine that burns a variety of fuels and requires no valves, cooling systems, radiators or mufflers, yet promises a thermodynamic efficiency of 75 percent.Co-founder of LiquidPiston with his father Nikolay, Dr. Shkolnik believes that the internal combustion engine is at the end of its development cycle.
 According to Shkolnik, after 150 years the ICE has made as many incremental improvements as it can. Many varieties of ICE, such as the Otto cycle used by petrol engines and the Diesel cycle, have had their successful points, but all fall short of being as efficient at they could be. Even what seem like very efficient engines, like the diesel, aren’t as good as they might appear.“Everyone would say at first glance that the diesel engine is more efficient (than the petrol engine). The truth is that if you had both engines at the same compression ratio, the spark-ignited engine has a faster combustion process and a more efficient process. In practice, it’s limited to a lower compression ratio otherwise you get spontaneous ignition.”
According to Shkolnik, after 150 years the ICE has made as many incremental improvements as it can. Many varieties of ICE, such as the Otto cycle used by petrol engines and the Diesel cycle, have had their successful points, but all fall short of being as efficient at they could be. Even what seem like very efficient engines, like the diesel, aren’t as good as they might appear.“Everyone would say at first glance that the diesel engine is more efficient (than the petrol engine). The truth is that if you had both engines at the same compression ratio, the spark-ignited engine has a faster combustion process and a more efficient process. In practice, it’s limited to a lower compression ratio otherwise you get spontaneous ignition.”
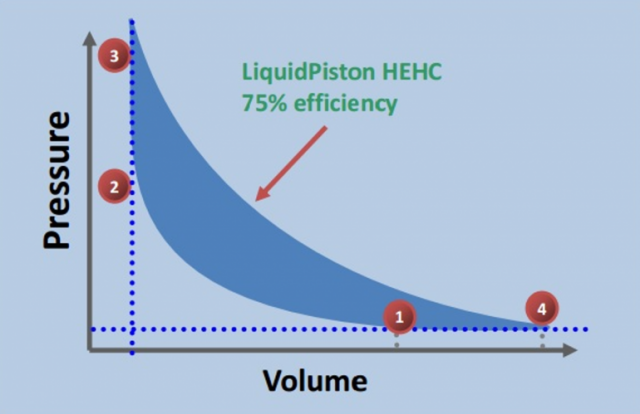
LiquidPiston’s approach to the problem was to go back to the basics of thermodynamics and work forward to develop what Shkolnik calls the “High Efficiency Hybrid Cycle” (HEHC), which combines the features of the Otto, Diesel, Rankine, and Atkinson cycles.
The idea is to compress the air in the LiquidPiston X2 engine to a very high ratio as in the diesel cycle and then isolating it in a constant volume chamber. When fuel is injected, it’s allowed to mix with the air and it auto-ignites as in a diesel engine, but the fuel/air mixture isn’t allowed to expand. Instead, it’s kept compressed in a constant volume so it can burn over an extended period, as in the Otto cycle. When the burning fuel/air mix is allowed to expand, it’s then overexpanded to near-atmospheric pressure. In this way, all the fuel is burned and almost all of the energy released is captured as work. Shkolnik calls this use of constant volume combustion “the holy grail of automotive engineering.”
Constant volume combustion and overexpansion provide an HEHC engine like the X2 with a number of benefits. Shkolnik points out that the X2 engine is exceptionally quiet because it burns all of its fuel. In current ICE engines, an alarming amount of fuel goes out the tailpipe. This not only cuts down on fuel efficiency and pollutes the air, it also makes the engine noisy. Since the X2 engine burns its fuel completely, there’s no need for complicated silencing apparatus.
The overexpansion used in the cycle also means that there is very little waste heat. An ICE only converts only 30 percent of its heat into work while the X2 engine has a thermal efficiency of 75 percent, so a water cooling system isn’t necessary. Water may be injected into an HEHC engine during compression or expansion for cooling, but doing so also helps to lubricate and seal the chamber and as the water cools the engine it converts into superheated steam, which boosts engine efficiency.
Shkolnik says that the X2 engine is a rotary because piston engines aren’t suitable for the HEHC and a rotary engine provides much more flexibility. Also, the use of a rotary design greatly simplifies the engine with only three moving parts and 13 major components required. That allows the X2 to be one-tenth the size of a comparable diesel engine.
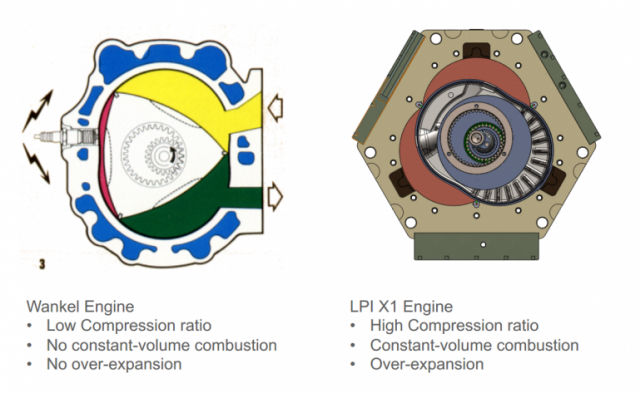 When asked whether the X2 engine isn’t just an updated Wankel, Shkolnik pointed out that though both are rotary engines, the Wankel is very different. For one thing, it uses a straightforward Otto cycle like a piston engine and operates at a much lower compression rate than the X2. In comparison, the X2 engine is almost the opposite of a Wankel. “It’s almost like the Wankel engine flipped inside-out,” said Shkolnik.
When asked whether the X2 engine isn’t just an updated Wankel, Shkolnik pointed out that though both are rotary engines, the Wankel is very different. For one thing, it uses a straightforward Otto cycle like a piston engine and operates at a much lower compression rate than the X2. In comparison, the X2 engine is almost the opposite of a Wankel. “It’s almost like the Wankel engine flipped inside-out,” said Shkolnik.
 Not only does the X2 engine work on a different principle from the Wankel, but it doesn’t suffer from the same limitations. The X2 engine has a better surface to volume ratio, it doesn’t have the thermodynamic limitations of the Otto cycle and it doesn’t have the emissions problems of the Wankel. The Wankel has apex seals that are carried around with the rotor and need to be lubricated. To do this, oil has to be sprayed on them, which means that the Wankel is burning oil as it runs, resulting in the high emissions that have recently curtailed its use. The X2 engine, on the other hand, moves the seals from the rotor to the crankcase, so no special lubrication is required.
Not only does the X2 engine work on a different principle from the Wankel, but it doesn’t suffer from the same limitations. The X2 engine has a better surface to volume ratio, it doesn’t have the thermodynamic limitations of the Otto cycle and it doesn’t have the emissions problems of the Wankel. The Wankel has apex seals that are carried around with the rotor and need to be lubricated. To do this, oil has to be sprayed on them, which means that the Wankel is burning oil as it runs, resulting in the high emissions that have recently curtailed its use. The X2 engine, on the other hand, moves the seals from the rotor to the crankcase, so no special lubrication is required.
Source: Gizmag

I have been in private business for 52 years.i have also been in the energy industry for 32 years.
We would like for one of your representative to reach out by calling 509 869 2188 PST or email below Regards William Evans ECI
I suggest that you click on the link to ‘Liquid Piston’ in the article – this will take you to their website, then choose ‘Contact’
I suggest that you click on the link to ‘Liquid Piston’ in the article – this will take you to their website, then choose ‘Contact’
I am wondering about the 70 hp unit for gasoline for motorcycle or dune buggy applications.
I suggest that you click on the link to ‘Liquid Piston’ in the article – this will take you to their website, then choose ‘Contact’